Vegetable Market Analysis
Analyzing the vegetable market reveals interesting insights into pricing trends, seasonal variations, and external factors affecting vegetable quality and supply. This analysis explores these dynamics through visually compelling data representations.
Key Findings
1. Price per kg of Vegetables
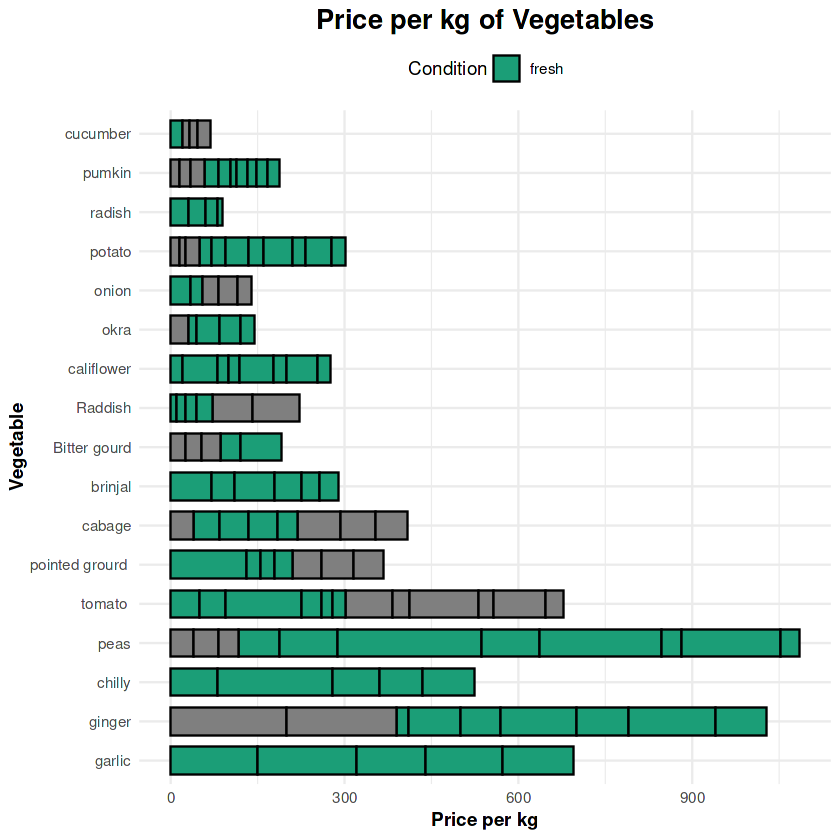
Fresh vegetables, including garlic, ginger, and peas, exhibit higher price ranges due to their demand and perceived quality. Lower prices are observed for seasonal or widely available items like potatoes and onions.
2. Impact of Natural Disasters on Prices
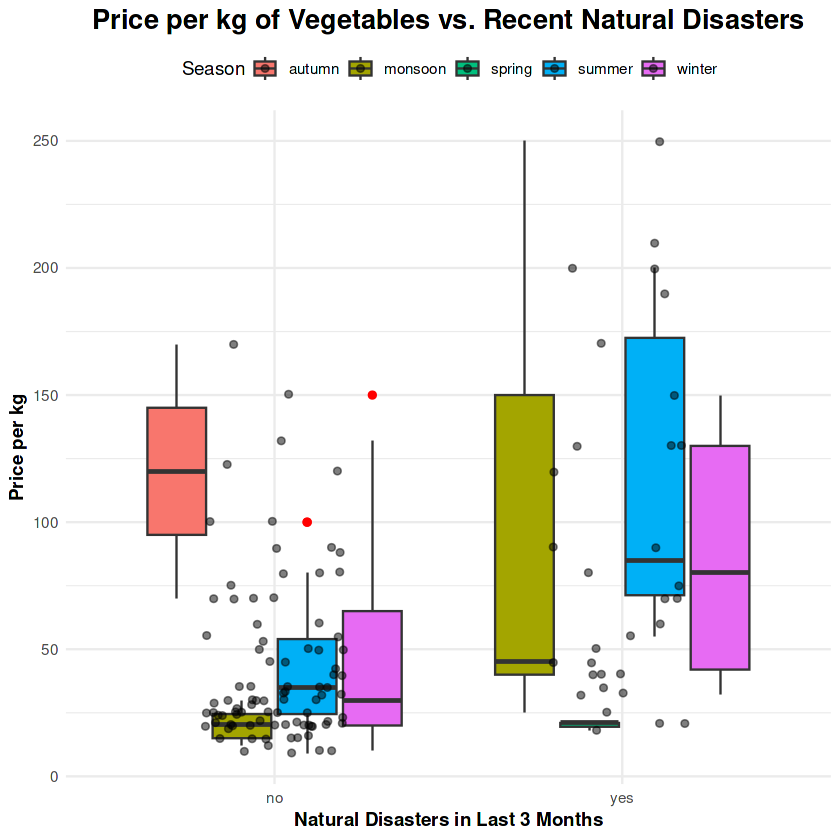
Natural disasters significantly increase vegetable prices, especially during monsoon seasons. Essential vegetables experience the highest price hikes, underlining supply chain vulnerabilities.
3. Temperature vs. Prices
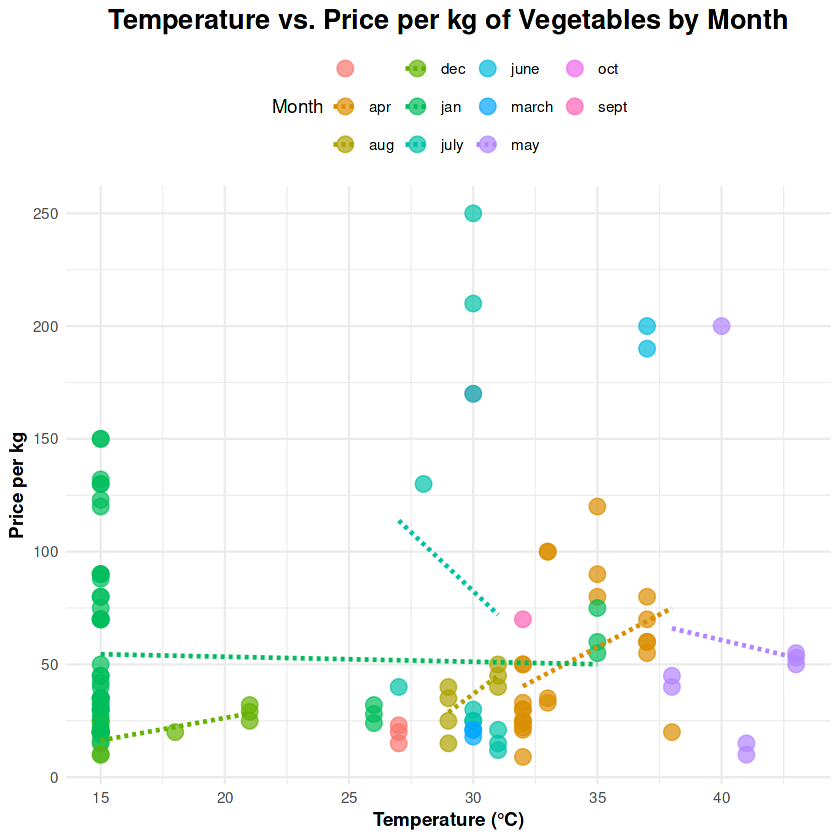
Temperature variations strongly influence vegetable prices. Cold-season produce, like cauliflower, commands higher prices during warmer months due to limited availability.
4. Seasonal Price Distribution
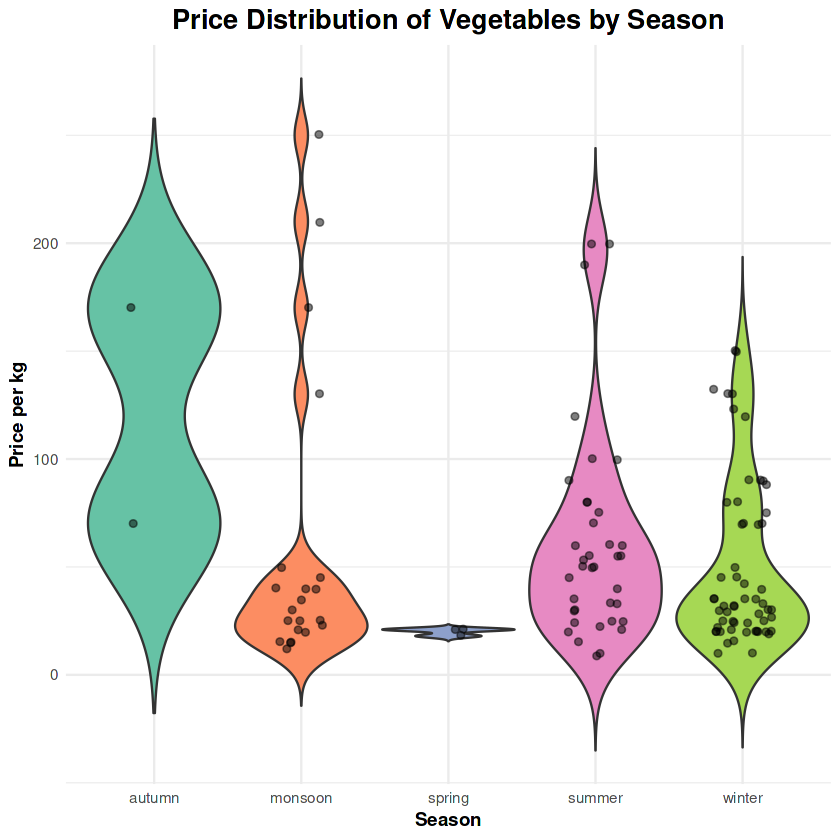
Autumn exhibits the highest price variance, while monsoons show minimal fluctuations. Seasonal availability plays a critical role in price stabilization or volatility.
5. Vegetable Condition and Natural Disasters
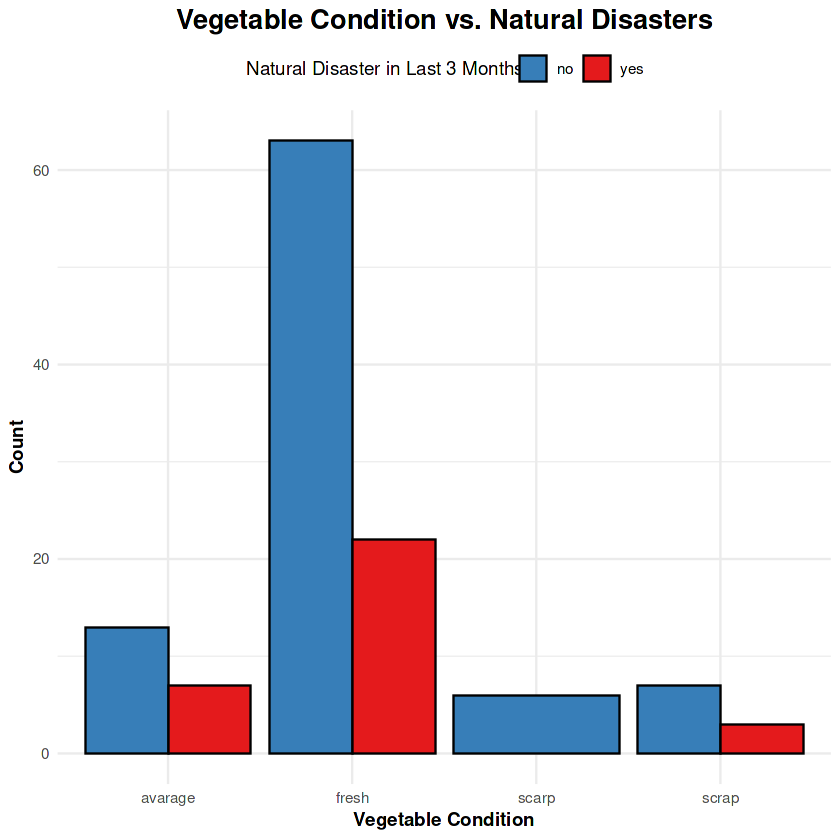
Fresh vegetables are more likely to be affected during disasters, leading to an increase in discarded or average-quality produce. This highlights the challenges of maintaining quality during adverse conditions.
6. Price by Condition
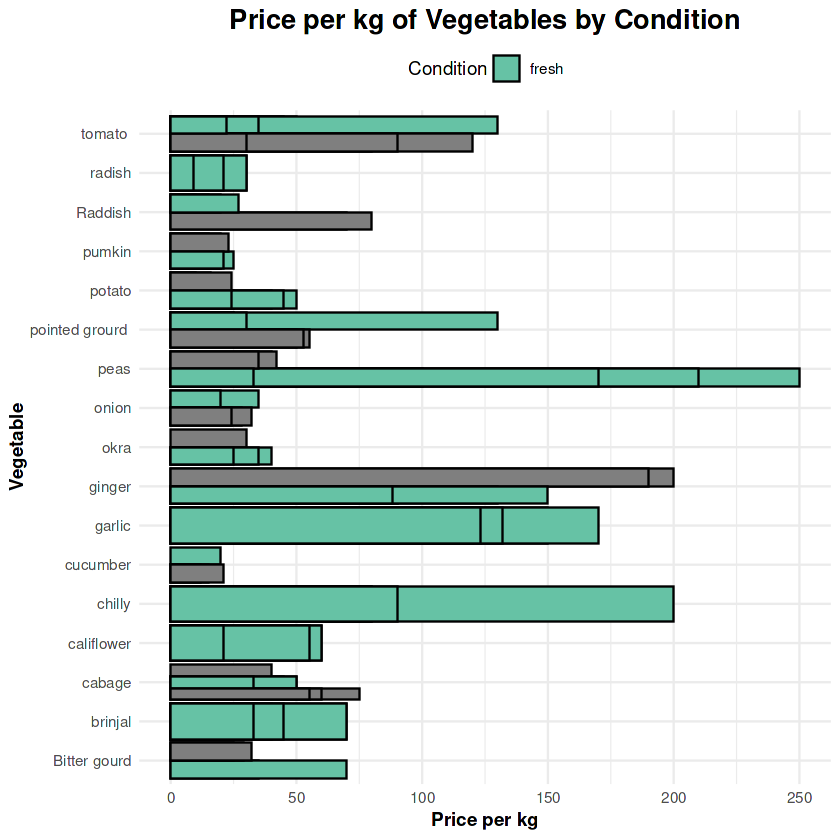
Fresh produce consistently achieves higher prices compared to average or discarded vegetables. Ginger and garlic show the steepest price differences.
7. Temperature Impact by Season
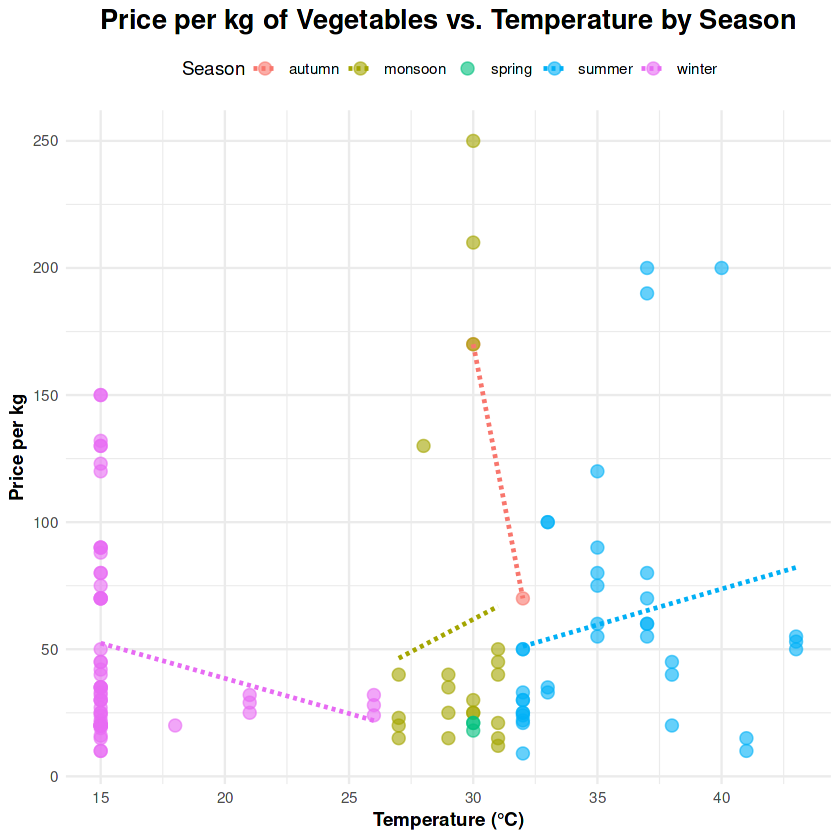
Seasonal temperature changes create noticeable price shifts, particularly for temperature-sensitive crops. Winter vegetables remain the most affected.
8. Fresh Vegetables by Season
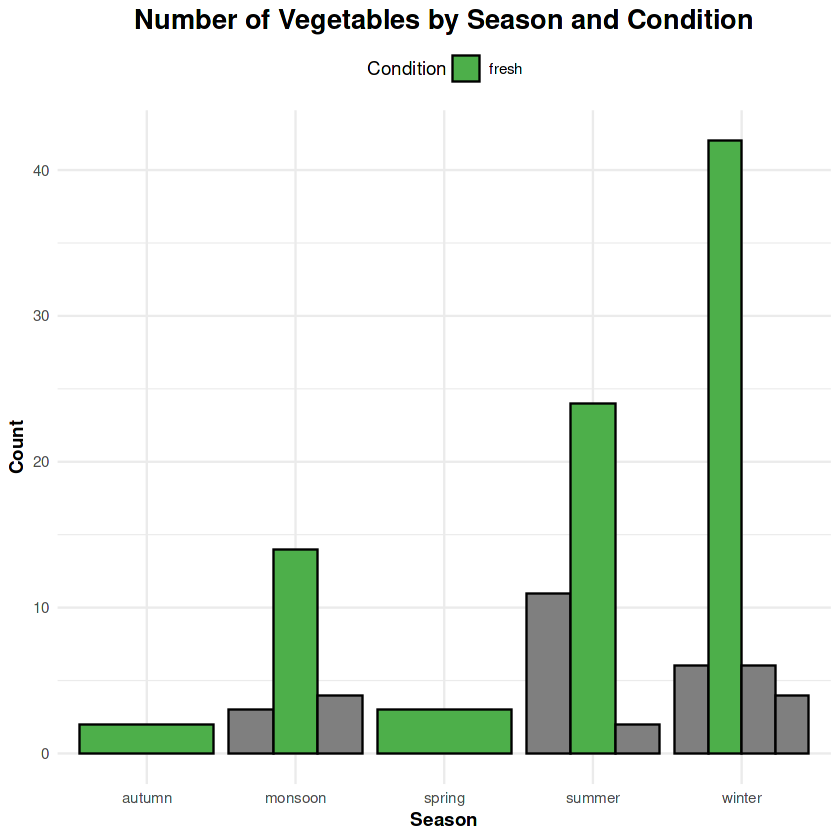
The availability of fresh vegetables peaks during winter and monsoon seasons, ensuring market stability. Scrap rates increase during hotter months.
9. Monthly Price Trends
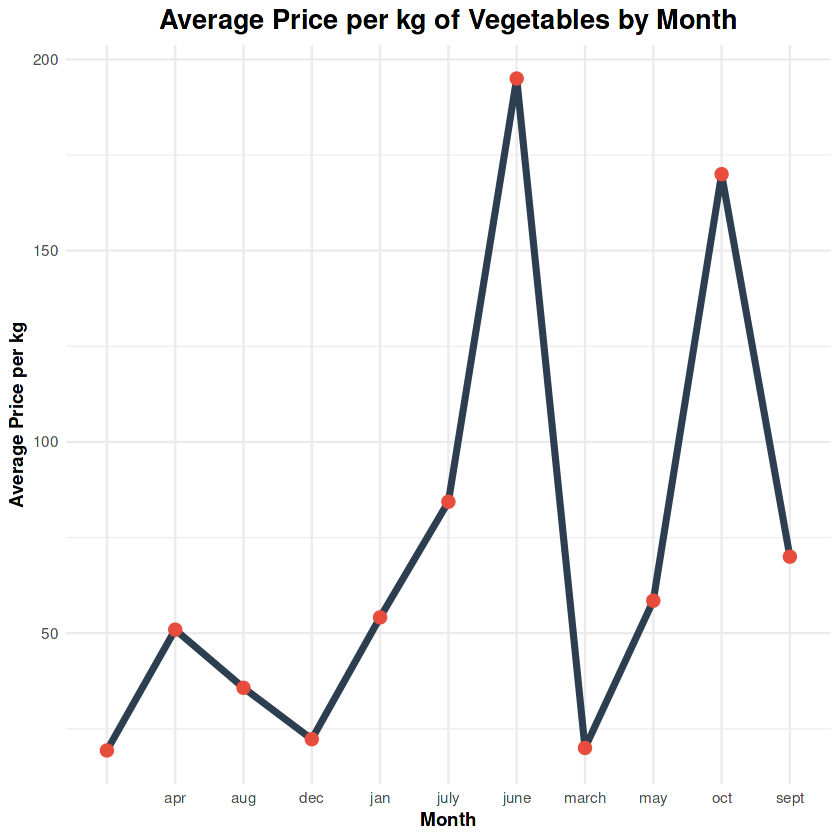
Monthly price trends show distinct peaks during July and October, likely influenced by seasonal demand and harvest schedules.
Conclusion
This analysis sheds light on key market dynamics:
- Fresh vegetables consistently command higher prices, emphasizing the importance of quality.
- Natural disasters and temperature changes disrupt supply chains and affect pricing.
- Seasonal patterns dictate market trends, creating predictable cycles for stakeholders.
These insights offer valuable guidance for farmers, distributors, and policymakers aiming to stabilize the vegetable market and optimize supply chains.
Code
For the complete code and additional analysis, visit: Vegetable Market Analysis on Kaggle